SAT Prep – Math: Geometry + Trigonometry
DSAT Math Content: Geometry and Trigonometry Domain
The digital SAT includes fewer geometry questions than the old SAT, but foundational knowledge is still required. A built‑in reference sheet provides essential formulas.
Core Skills:
- Area and perimeter of polygons
- Circles: radius, diameter, arc lengths
- Coordinate geometry (slope, midpoint, distance)
- Volume of cylinders, cones, spheres
- Right‑triangle trigonometry
- Transformations and geometric reasoning
Example
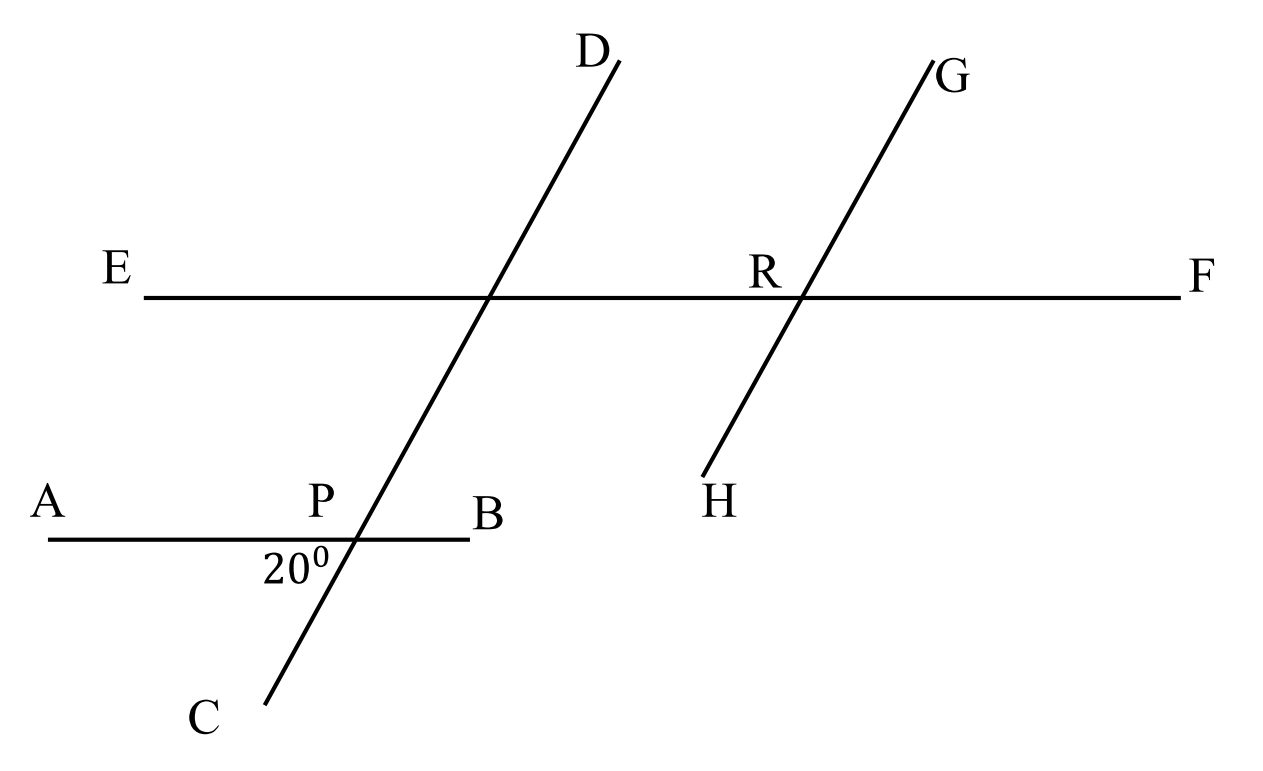
In the given figure above, $AB{\parallel}EF$, $CD{\parallel}GH$ and points P, Q and R are intersection points of the lines. If $\angle APC=20$°, what is the measurement of $\angle GRF$ (in degrees)?
Solution
As $AB{\parallel}EF$, $\angle APC=\angle EQC$ (corresponding angles) ... (1)
Now, $\angle EQC=\angle DQF$ (vertically opposite angles) ... (2)
Also, $CD{\parallel}GH$. So, $\angle DQF=\angle GRF$ (corresponding angles) ... (3)
From equation (1), (2) and (3); we can say that $\angle APC=\angle GFR$
As, $\angle APC=20$°
Hence, $\angle GFR=20$°
The correct answer is 20.
Applications:
- Engineering and Architecture
- Navigation and Mapping
- Physics and Motion
- Everyday Quantitative Tasks
Tools on SAT:
- Reference sheet for geometry formulas
- Built‑in graphing calculator
